ECG-Treadmill Test (TMT): A Vital Diagnostic Tool for Heart Health
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the critical role of the ECG-Treadmill Test (TMT) in assessing cardiovascular health. Under the expert guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this diagnostic tool to evaluate heart function, detect abnormalities, and guide treatment decisions.
.
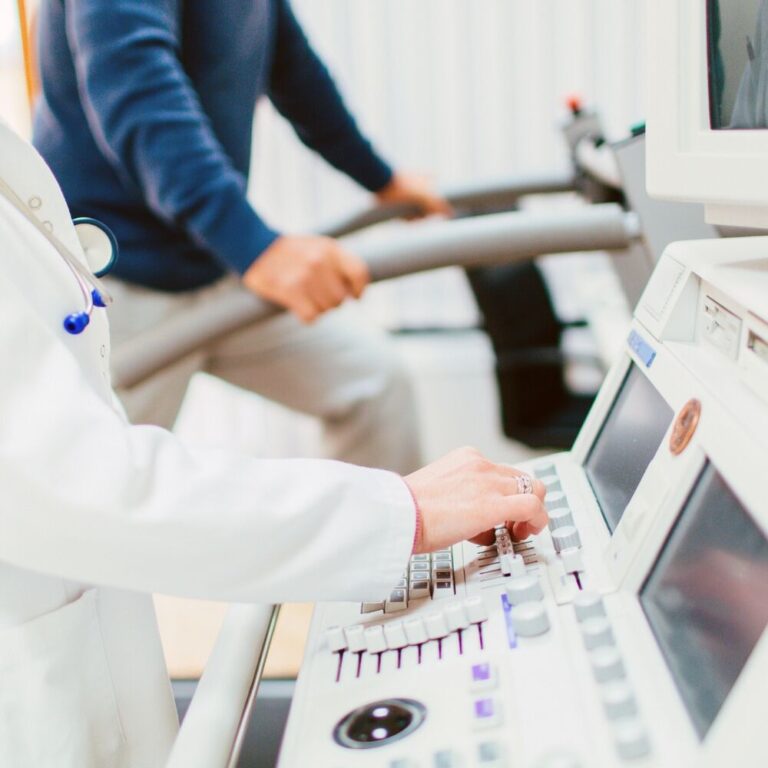

Understanding ECG-Treadmill Test (TMT)
What is TMT?
The TMT, also known as a stress test, combines two essential components: electrocardiography (ECG) and treadmill exercise. This non-invasive procedure helps us assess how your heart responds to physical stress, simulating real-world conditions.
The Procedure
- Electrodes Placement: Small electrodes are attached to your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes record your heart’s electrical activity during the test.
- Treadmill Exercise: You walk or run on a treadmill while the speed and incline gradually increase. This mimics the stress your heart experiences during physical activity.
- Continuous Monitoring: The ECG machine continuously monitors your heart rate, rhythm, and any changes in the ECG pattern.
- Interpretation: Dr. Ramteke and our team analyze the ECG data, looking for signs of reduced blood flow, abnormal heart rhythms, or other indicators of heart disease.
Why ECG-Treadmill Test?
- Detecting Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): TMT helps identify reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, a common sign of CAD.
- Assessing Exercise Capacity: It evaluates your heart’s ability to handle physical stress. Abnormal responses may indicate underlying issues.
- Monitoring Arrhythmias: TMT detects irregular heart rhythms during exercise, providing valuable insights.
- Guiding Treatment Decisions: Based on the test results, Dr. Ramteke tailors treatment plans to your specific needs.
Trust Dr. Rahul Ramteke
Dr. Ramteke’s expertise in interpreting TMT results ensures accurate diagnoses. His commitment to staying informed about advancements in cardiology guarantees that the patient receives the best and advanced cardiac care available.
Your Heart Matters
Whether you’re seeking preventive screening or managing existing heart conditions, our ECG-Treadmill Test is a crucial tool. Trust Dr. Ramteke and our team to safeguard your heart health. Schedule your TMT today and take a step toward a healthier future.
Holter Monitoring: A Window into Your Heart’s Rhythm
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the importance of Holter monitoring in understanding your heart’s behavior beyond the confines of a clinical visit. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this powerful diagnostic tool to gain insights into your heart’s rhythm, detect irregularities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
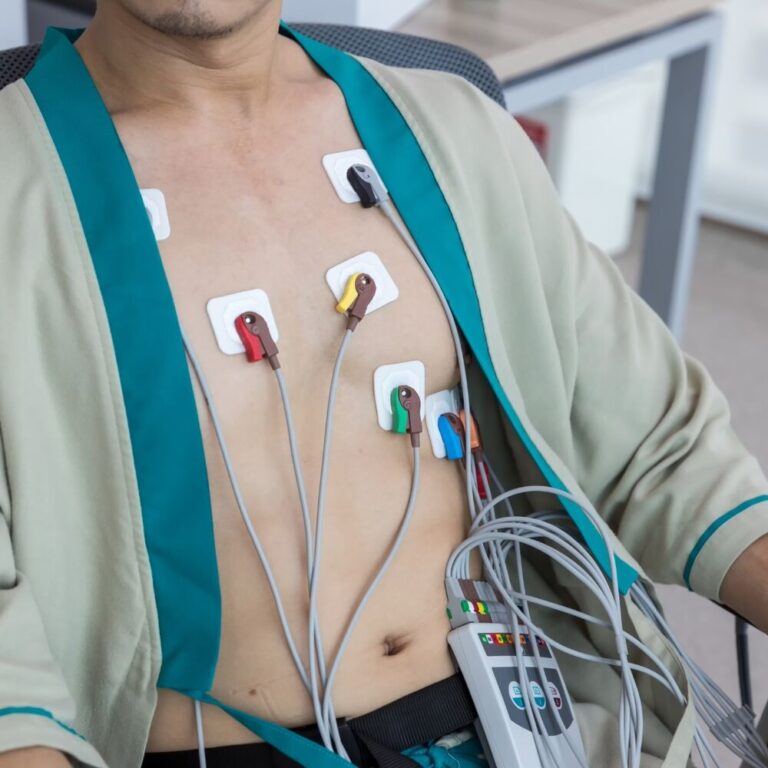
What Is Holter Monitoring? Continuous Heart Monitoring
The Holter monitor is a portable device that records your heart’s electrical activity over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours and max 7 days. Unlike a standard ECG, which captures a snapshot of your heart’s rhythm, the Holter monitor provides a continuous stream of data.
The Procedure
- Wearable Device: You’ll wear the Holter monitor as you go about your daily activities. It’s discreet and won’t interfere with your routine.
- Electrodes Placement: Small electrodes are attached to your chest. These electrodes transmit signals to the monitor, capturing every heartbeat.
- Data Collection: The monitor records your heart’s electrical patterns, including any irregularities, palpitations, or symptoms you may experience.
- Analysis: Dr. Ramteke and our team meticulously analyze the recorded data. We look for abnormal rhythms, silent ischemia (lack of blood flow to the heart), and other relevant information.
Why Holter Monitoring?
- Detecting Arrhythmias: Holter monitoring is invaluable for identifying irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Whether it’s atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, or tachycardia, we can pinpoint the issue.
- Assessing Symptoms: If you experience unexplained dizziness, palpitations, or fainting spells, the Holter monitor captures these events, aiding diagnosis.
- Evaluating Treatment Effectiveness: For patients with known heart conditions, Holter monitoring helps assess the effectiveness of medications or interventions.
- Tailoring Treatment Plans: Armed with detailed data, Dr. Ramteke customizes treatment plans to address your specific needs. Be it medicine or device therapy or EPS/RFA surgery.
Your Heart Deserves Attention
Whether you’re seeking answers to puzzling symptoms or need ongoing monitoring, our Holter monitoring service provides clarity. Trust Dr. Ramteke and our team to safeguard your heart health. Schedule your Holter monitoring today and gain valuable insights into your heart’s rhythm.
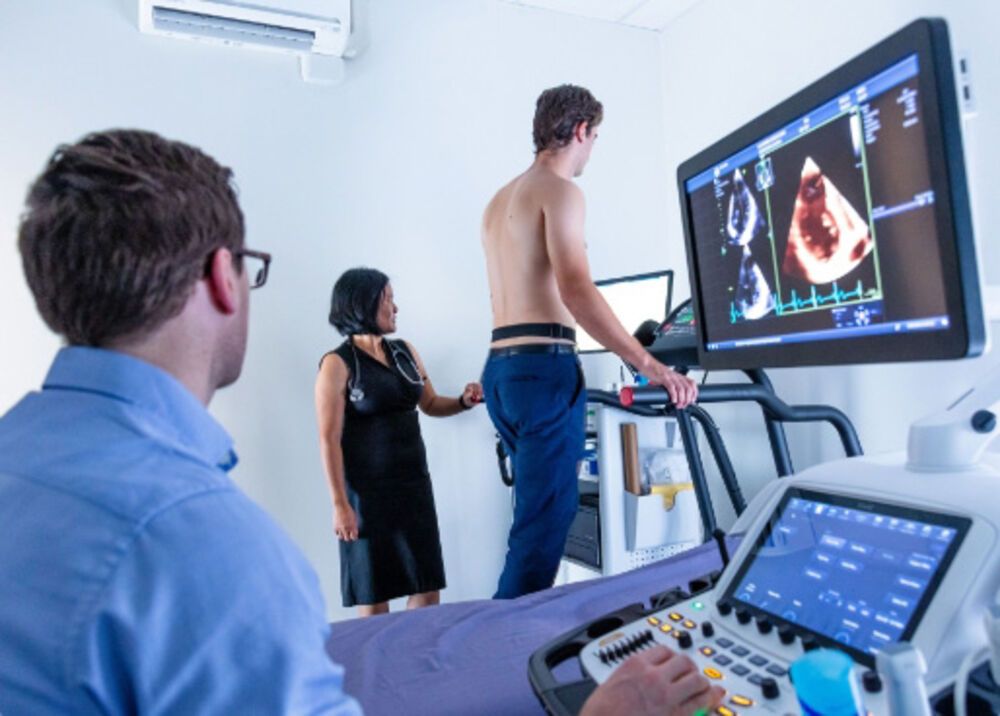
Stress Echocardiography: A Window into Heart Function
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the significance of Stress Echocardiography in assessing cardiac health. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this advanced diagnostic technique to gain valuable insights into heart function, detect abnormalities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
Understanding Stress Echocardiography
What Is Stress Echocardiography?
Stress Echocardiography combines two essential components: echocardiography (echo) and physical stress. This non-invasive procedure allows us to evaluate how your heart responds to exertion, providing crucial information about blood flow, muscle function, and overall cardiac performance.
The Procedure
- Echocardiography: During rest, we perform a standard echocardiogram, capturing detailed images of your heart’s structure and function using ultrasound waves.
- Physical Stress: You’ll undergo controlled physical stress, either through exercise (treadmill or bicycle) or medication (if exercise is not feasible). This mimics real-world conditions and challenges your heart.
- Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the stress phase, we monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG. The echo machine captures images during stress and recovery.
- Comparison: By comparing pre- and post-stress images, we assess any changes in blood flow, wall motion, and valve function.
Why Stress Echocardiography?
- Detecting Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Stress echo helps identify reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, a hallmark of CAD.
- Assessing Heart Function: It evaluates how well your heart pumps blood during stress. Abnormalities may indicate underlying issues.
- Diagnosing Valve Problems: Stress echo detects valve abnormalities, such as stenosis or regurgitation.
- Guiding Treatment Decisions: Based on the test results, Dr. Ramteke tailors treatment plans to optimize your heart health.
Your Heart Deserves Precision
Whether you’re seeking early detection, monitoring, or personalized treatment, our Stress Echocardiography service provides clarity. Trust Dr. Ramteke and our team to safeguard your heart’s well-being. Schedule your stress echo today and gain valuable insights into your cardiac function.

Ambulatory BP Monitoring
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the significance of Ambulatory BP Monitoring in assessing cardiac health. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this advanced diagnostic technique to gain valuable insights into heart function, detect abnormalities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) is a diagnostic procedure used to measure blood pressure (BP) continuously over a 24-hour period. It involves wearing a portable BP monitor that automatically takes multiple BP readings at set intervals throughout the day and night.
Procedure: During an ABPM session, the patient wears a compact, portable BP monitor that is typically strapped to the upper arm. The monitor is connected to a cuff that inflates and deflates automatically to measure BP. The patient carries out their usual daily activities, including work, exercise, and sleep, while wearing the monitor. The monitor is programmed to take BP readings at regular intervals, usually every 15 to 30 minutes during waking hours and every 30 to 60 minutes during sleep. After the monitoring period (usually 24 hours), the patient returns the device to the healthcare provider’s office for data analysis.
Purpose: ABPM serves several purposes:
- It provides a more comprehensive assessment of a patient’s BP patterns compared to occasional office-based measurements, offering insights into BP fluctuations throughout a typical day.
- It helps diagnose and monitor hypertension (high BP), particularly in individuals with suspected white coat hypertension (elevated BP in a clinical setting but normal BP outside of it), masked hypertension (normal BP in a clinical setting but elevated BP outside of it), or nocturnal hypertension (elevated BP during sleep).
- It assists in tailoring individualized treatment plans for hypertension management by providing objective evidence of BP levels and patterns.
- It may improve patient adherence to treatment by offering real-time feedback on BP control and response to antihypertensive medications.
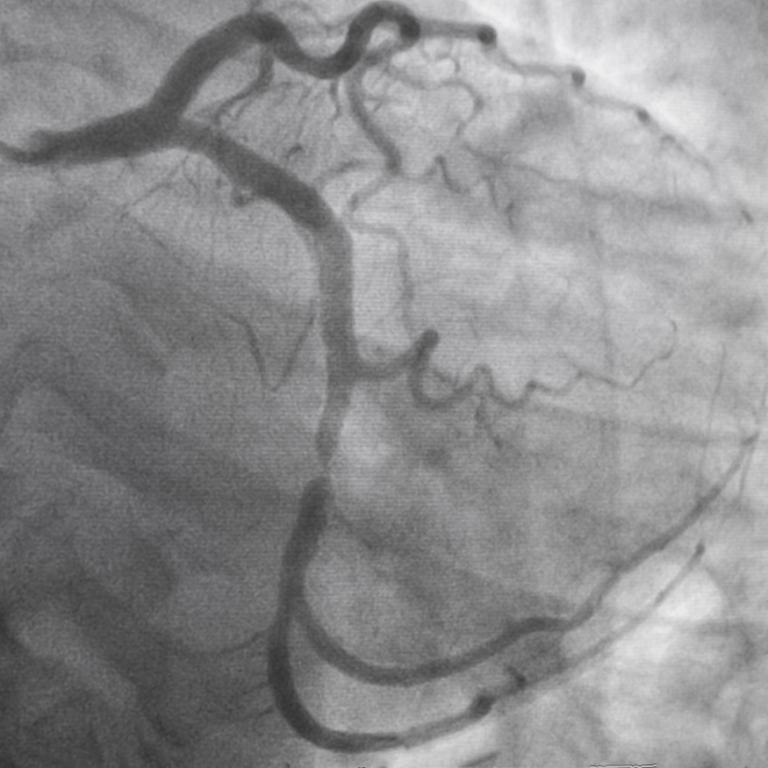
Angiogram
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the significance of Angiogram in assessing cardiac health. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this advanced diagnostic technique to gain valuable insights into heart function, detect abnormalities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
Angiogram, also known as angiography or arteriography, is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the blood vessels (arteries and veins) in various parts of the body. It involves the use of contrast dye and imaging techniques to assess the structure, function, and blood flow within the blood vessels.
Procedure: During an angiogram, a special dye called contrast material is injected into the bloodstream through a thin, flexible tube called a catheter. The catheter is typically inserted into a large blood vessel, such as the femoral artery in the groin or the radial artery in the wrist, under local anesthesia. The catheter is then carefully threaded through the blood vessels to the area of interest, guided by fluoroscopy or X-ray imaging.
Once the catheter is in position, the contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the blood vessels, allowing them to be visualized on X-ray images or other imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These images provide detailed information about the size, shape, and condition of the blood vessels, as well as any abnormalities such as blockages, narrowing (stenosis), or aneurysms.
After the imaging is complete, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding. The patient is typically monitored for a short period following the procedure to ensure there are no complications.
Purpose: Angiography serves several purposes:
- Diagnosis: It helps diagnose various vascular conditions, including arterial blockages, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
- Assessment: It provides detailed information about the location, severity, and extent of vascular abnormalities, aiding in treatment planning and decision-making.
- Intervention: In some cases, angiography can be used as a therapeutic tool to treat certain vascular conditions. For example, interventional procedures such as angioplasty, stent placement, embolization, or thrombectomy can be performed during angiography to restore blood flow or address abnormalities detected during the procedure.
- Monitoring: Angiography may be repeated periodically to monitor the progression of vascular diseases, assess the effectiveness of treatment, or detect any new abnormalities.
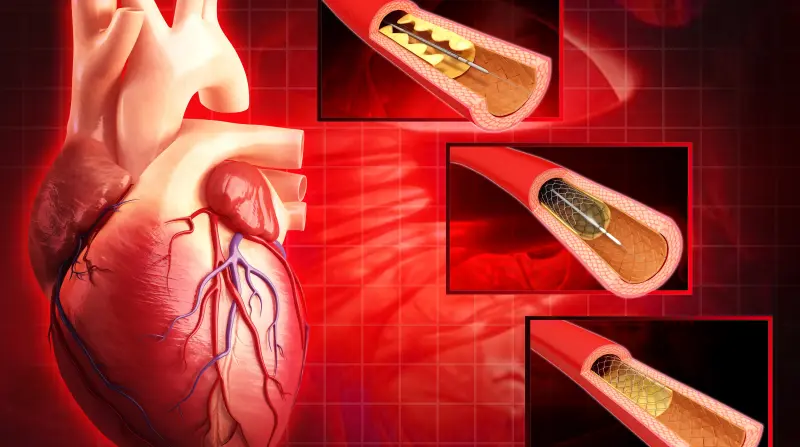
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization, also known as coronary angiography or heart catheterization, is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the function and structure of the heart and its blood vessels. It involves inserting a thin, flexible tube (catheter) into a blood vessel in the arm, groin, or neck and threading it through to the heart under X-ray guidance. This allows healthcare providers to visualize the coronary arteries, heart chambers, and valves, as well as measure pressures within the heart.
Procedure:
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient may receive sedation or anesthesia to help them relax and minimize discomfort. The healthcare team cleans and numbs the area where the catheter will be inserted.
- Insertion of Catheter: The healthcare provider makes a small incision in the skin and inserts a catheter into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or wrist. They carefully thread the catheter through the blood vessels until it reaches the heart.
- Injection of Contrast Dye: Once the catheter is in place, contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the coronary arteries or heart chambers. The dye helps visualize the blood vessels and heart structures on X-ray images.
- Imaging: X-ray images (angiograms) are taken as the contrast dye flows through the blood vessels. The healthcare provider examines the images to assess blood flow, detect blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries, evaluate heart chamber size and function, and assess the function of heart valves.
- Pressure Measurements: During the procedure, pressure measurements may be taken inside the heart chambers to evaluate heart function and assess for abnormalities such as high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension) or narrowing of heart valves.
- Completion: Once the necessary images and measurements have been obtained, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding. The patient is monitored for a short period afterward to ensure there are no complications.
Purpose: Cardiac catheterization serves several purposes:
- Diagnosis: It helps diagnose various heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, congenital heart defects, and cardiomyopathy.
- Assessment of Coronary Arteries: It allows visualization of the coronary arteries to identify blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities that may affect blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Evaluation of Heart Function: It provides information about heart chamber size, wall motion, and overall heart function, which can help guide treatment decisions.
- Treatment: In some cases, cardiac catheterization may be used to perform certain interventional procedures, such as balloon angioplasty to open blocked arteries, stent placement to keep arteries open, or valve repair or replacement.
- Risk Stratification: It helps assess the severity of heart disease and determine the risk of future cardiovascular events such as heart attack or stroke.
Cardiac MRI
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the significance of Cardiac MRI in assessing cardiac health. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this advanced diagnostic technique to gain valuable insights into heart function, detect abnormalities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
Cardiac MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to obtain detailed images of the heart and surrounding structures. It utilizes a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create cross-sectional images of the heart, allowing healthcare providers to assess its structure, function, and blood flow. Cardiac MRI provides valuable diagnostic information for a variety of cardiovascular conditions, including congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, valve disorders, and myocardial infarction.
Procedure: During a cardiac MRI procedure, the patient lies on a table within a large cylindrical machine called an MRI scanner. The scanner generates a strong magnetic field and emits radio waves, which interact with hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues to produce images. Before the scan begins, the patient may receive an injection of a contrast agent (such as gadolinium) to enhance the visibility of blood vessels and cardiac structures.
The patient must remain still during the scan to avoid blurring of the images. The MRI technologist may provide instructions or use positioning aids to help the patient maintain the correct position. The scanner makes loud knocking or tapping noises during the imaging process, but earplugs or headphones may be provided to reduce discomfort.
The actual scanning process typically takes around 30 to 60 minutes, during which time multiple images are acquired from different angles and planes. The technologist may ask the patient to hold their breath briefly during certain sequences to minimize motion artifacts.
Once the scan is complete, a radiologist or cardiologist interprets the images to evaluate the heart’s structure, function, and blood flow. The findings are then used to diagnose and guide the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions.
Purpose: Cardiac MRI serves several purposes:
- Diagnostic Imaging: It provides detailed images of the heart’s anatomy, including the chambers, valves, and blood vessels, allowing healthcare providers to identify abnormalities or pathology.
- Functional Assessment: It assesses the heart’s function, such as ejection fraction (a measure of pumping efficiency) and myocardial strain (a measure of heart muscle function), aiding in the diagnosis and management of heart conditions.
- Blood Flow Evaluation: It evaluates blood flow within the heart and surrounding vessels, helping to detect abnormalities such as stenosis (narrowing) or aneurysms (weakness or bulging) in blood vessels.
- Treatment Planning: It assists in treatment planning for various cardiovascular interventions, such as cardiac surgery, angioplasty, or valve replacement, by providing accurate anatomical and functional information.
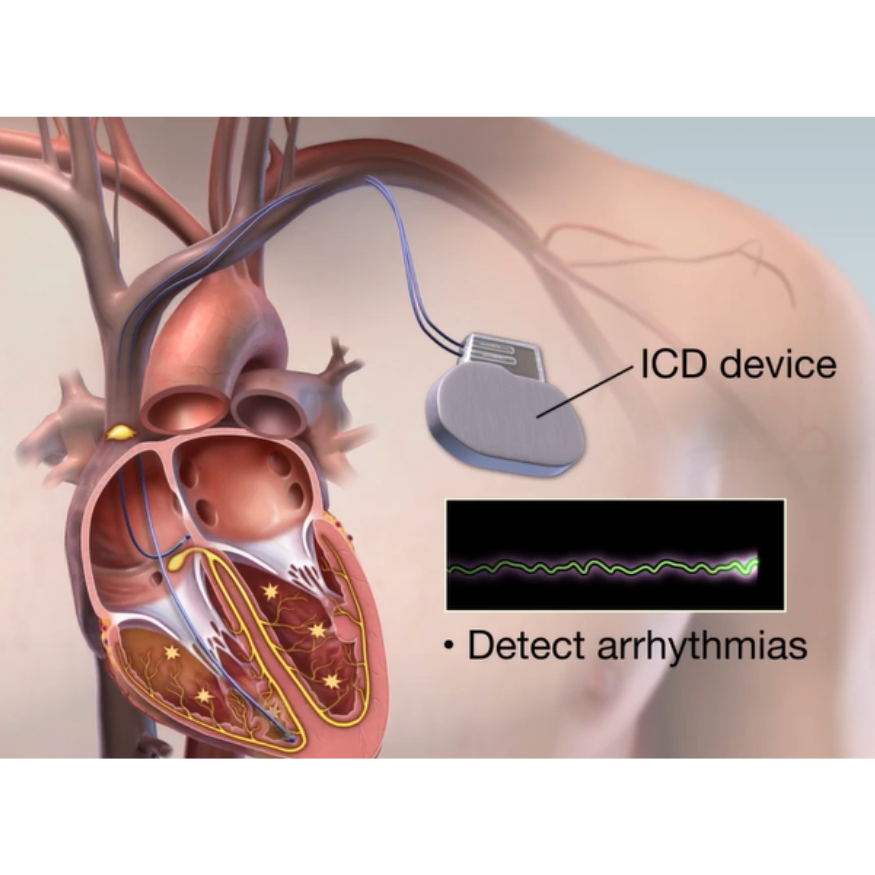
Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, (AICD)
At Atrioum Chamber, R Block, Dilshad Garden, Delhi, we recognize the significance of AICD in assessing cardiac health. Under the guidance of Dr. Rahul Ramteke, our team utilizes this advanced diagnostic technique to gain valuable insights into heart function, detect abnormalities, and tailor personalized treatment plans.
An Automatic Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (AICD), also known as an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD), is a small electronic device implanted under the skin to monitor and regulate the heart’s rhythm. It is designed to treat life-threatening arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) and ventricular fibrillation (rapid, erratic heartbeat), by delivering electrical shocks or pacing pulses to restore a normal heart rhythm.
Procedure: The implantation of an AICD involves a surgical procedure performed in a hospital setting. Here’s an overview of the procedure:
- Preparation: The patient is prepared for surgery by fasting for several hours and undergoing pre-operative assessments, including blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), and imaging studies.
- Anesthesia: The patient is administered anesthesia to induce sedation or general anesthesia to ensure comfort and minimize pain during the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision, usually on the left side of the chest below the collarbone, to access the blood vessels and create a pocket under the skin for the AICD device.
- Lead Placement: Thin, insulated wires (leads) are inserted through veins and guided to the heart chambers. These leads sense the heart’s electrical activity and deliver electrical shocks or pacing pulses when needed.
- Device Implantation: The AICD device is placed in the pocket created under the skin, and the leads are connected to the device.
- Testing: Once the device is implanted, the surgeon tests its functionality by inducing controlled arrhythmias and verifying the device’s ability to detect and treat them appropriately.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the surgical site.
- Recovery: The patient is monitored closely in a recovery area to ensure stability and recovery from anesthesia. Pain management medications may be provided as needed.
- Post-operative Care: The patient receives instructions on caring for the surgical incisions, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider.
Purpose: AICDs serve several purposes in managing cardiac arrhythmias:
- Treatment of Life-Threatening Arrhythmias: AICDs are designed to deliver electrical shocks or pacing pulses to terminate dangerous arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, which can lead to sudden cardiac arrest if left untreated.
- Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: By restoring normal heart rhythm promptly during arrhythmic events, AICDs can prevent sudden cardiac death in individuals at high risk due to underlying heart conditions.
- Monitoring and Recording: AICDs continuously monitor the heart’s rhythm and store data on arrhythmic events, providing valuable information for diagnostic purposes and treatment optimization.
- Adaptability: AICDs can be programmed and adjusted remotely by healthcare providers to optimize therapy settings and adapt to changes in the patient’s condition over time.



